Ventriculoperitoneal shunts are vital medical devices used to treat hydrocephalus, a condition characterised by excess fluid buildup in the brain. These shunts play a crucial role in managing this and other related conditions by diverting the fluid to another part of the body where it can be absorbed. They are typically needed when hydrocephalus causes symptoms like headaches, nausea, or vision problems and other treatments have not been effective.
Understanding when a VP shunt might be necessary in detail can help individuals and their healthcare providers make informed decisions about treatment options.
What is a VP Shunt?
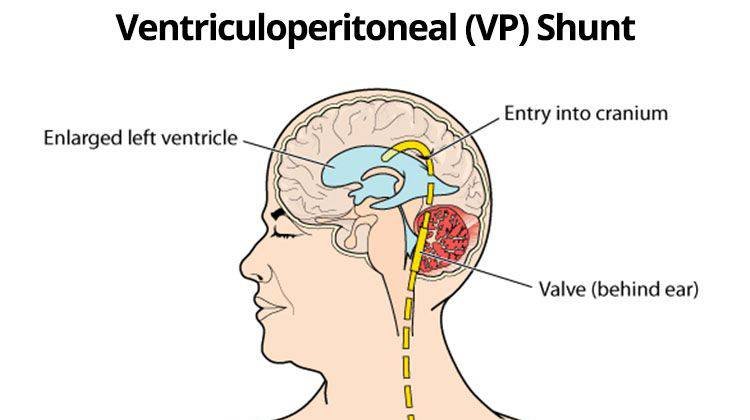
A VP shunt, also known as a ventriculoperitoneal shunt, is a medical device used to treat hydrocephalus, a condition in which excess cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) accumulates in the brain. This procedure involves placing a tube that diverts the extra fluid from the brain to the abdominal cavity, where the body can absorb it. This helps relieve pressure in the brain and reduces symptoms.
There are two types of VP shunts: programmable and non-programmable. Programmable shunts allow for adjustments without additional surgery, while non-programmable ones have a fixed flow rate. Both types are effective in managing hydrocephalus and alleviating symptoms such as headaches and vision problems.
When Do You Need a VP Shunt?
A VP shunt is typically required when abnormal CSF accumulation, known as hydrocephalus, occurs. This can be due to congenital abnormalities, infections, tumours, or brain injuries.
For infants and children with congenital hydrocephalus, the condition might cause an enlarged head, developmental delays, and other neurological issues. In these cases, a VP shunt is essential to drain the excess fluid and relieve pressure on the brain.
In adults, hydrocephalus may result from conditions like intraventricular haemorrhage, meningitis, or traumatic brain injury. Symptoms can include severe headaches, cognitive impairments, and difficulty walking. A VP shunt helps manage these symptoms by diverting CSF to the abdominal cavity.
Dr. Vikas Gupta explains, “The need for a VP shunt is determined by the underlying cause of hydrocephalus and the severity of symptoms. It is typically recommended when other treatments, such as medication or less invasive procedures, have not been effective in controlling the condition and relieving symptoms.”
What is the Cost of a VP Shunt in India?
The cost of VP shunt surgery in India generally ranges from INR 50,000 to INR 2,00,000, approximately $700 to $2,800. This cost can vary based on factors such as the hospital, location, type of shunt, and additional medical expenses. Consulting healthcare providers or hospitals directly is advisable for accurate pricing information.
What Are the Benefits and Risks of VP Shunt Surgery?
Benefits:
- Symptom Relief: Alleviates headaches, nausea, and vision problems.
- Improved Quality of Life: Helps individuals return to their daily activities.
- Prevents Brain Damage: Reduces pressure on the brain, preventing further complications.
- Effective Treatment: Successful in managing hydrocephalus when other treatments fail.
Risks:
- Infection: Risk of infection at the shunt site.
- Malfunction: The shunt may become blocked or dislodged, requiring surgery to fix it.
- Overdrainage: Potential for low-pressure headaches or subdural hematoma.
- Underdrainage: Inadequate fluid drainage, which may necessitate shunt revision.
- Mechanical Failure: Components of the shunt can break or fail over time.
Dr Vikas Gupta emphasises, “It’s essential to weigh the benefits against the risks and discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider. Regular follow-up care is crucial to monitor the shunt’s function and address any issues promptly.”
Ramesh Sharma shares, “I was suffering from severe headaches and blurred vision due to hydrocephalus. After getting a VP shunt implanted, my symptoms have significantly improved. I am grateful to Dr. Vikas Gupta for his expertise and care.”
Preeti Singh adds, “My daughter was born with congenital hydrocephalus, and we were worried about her future. Thanks to the VP shunt surgery performed by Dr. Gupta, she is now thriving and living a normal life. We are thankful for his skill and compassion.”
Conclusion
A VP shunt is a crucial treatment for managing hydrocephalus. It is needed when other methods fail to alleviate symptoms caused by excess cerebrospinal fluid in the brain. This procedure is a safe and effective intervention that can significantly enhance a patient’s quality of life. If you or a loved one experiences symptoms such as headaches, vomiting, or vision problems, consult a healthcare professional to determine if this device is appropriate. Early diagnosis and intervention are essential to successful treatment.
FAQs
1. Can you live a normal life with a VP shunt?
Yes, with proper care and monitoring, people with VP shunts can lead normal lives.
2. What activities should be avoided with a VP shunt?
To prevent damage to the VP shunt, contact sports and activities with a high risk of head injury should be avoided.
3. Will there be a scar after VP shunt surgery?
Yes, the VP shunt surgery typically leaves a small scar where the shunt is inserted. The size and visibility of the scar can vary depending on the surgical technique and individual healing process. Proper wound care can help minimise scar formation.
4. How often should a VP shunt be checked?
A VP shunt should be checked regularly, typically every 6 to 12 months, with a healthcare provider to monitor its function and address any issues promptly.
5. How long does a VP shunt last?
The lifespan of a VP shunt can vary, but it typically lasts between 5 to 10 years before requiring replacement.
Explore more blogs: Is Brain Tumor Surgery Safe? Understanding the Risks and Benefits
