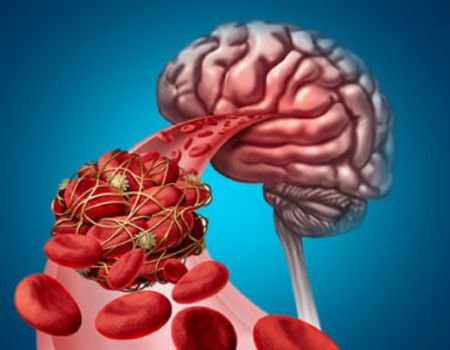
In recent years, doctors and researchers have observed a noticeable increase in cases of brain clots, also known as blood clots in the brain or cerebral thrombosis. While once considered a condition predominantly affecting the elderly, younger people are now also being diagnosed with this potentially life-threatening problem.
So, why is this happening? What are the warning signs? And how can we respond quickly?
While once considered a condition predominantly affecting the elderly, younger people are now also being diagnosed with this potentially life-threatening problem.
So, why is this happening? What are the warning signs? And how can we respond quickly?
Let’s explore the answers to these important questions.
What Is a Brain Clot?
A brain clot occurs when a blood clot forms in the brain’s blood vessels, blocking the flow of oxygen-rich blood. This obstruction can lead to a stroke, which may cause permanent brain damage or even death.
This condition is often referred to as cerebral thrombosis, and it typically results from damage to blood vessels or abnormal clotting.
Why Are Brain Clots Becoming More Common?
Several interconnected factors are driving the increase in brain clot cases:
- Sedentary Lifestyles: With more time spent sitting (especially during work-from-home setups), blood circulation is compromised, increasing clotting risk.
- Obesity & Diet: A poor diet high in saturated fats and sugar raises cholesterol, damaging blood vessels over time.
- Stress and Hypertension: Chronic stress elevates blood pressure, one of the top stroke causes.
- Smoking and Alcohol: These substances harm blood vessels and can make blood more prone to clotting.
- COVID-19: The virus increases inflammation and clotting tendencies in some patients.
- Contraceptives: Certain birth control pills slightly increase the risk of clot formation, especially in women who smoke.
With more people being diagnosed earlier due to increased health awareness and better imaging technology, it’s no surprise that brain clot cases are rising.
Can Young People Get Brain Clots?
Absolutely. One of the most alarming trends is the growing number of young adults. Even teenagers nowadays get diagnosed with brain clots, which was previously rare; blood clots in the brain among people under 40 are becoming more common.
Risk factors in young people include:
- Genetic clotting disorders
- Sedentary screen time
- Energy drink or stimulant overuse
- Use of oral contraceptives or steroids
- Smoking or vaping
- Post-COVID complications
Dr. Vikas Gupta, a leading neurologist, warns:
“We’re seeing an unprecedented rise in stroke cases among people in their 20s and 30s. Poor lifestyle choices, excessive screen time, and undiagnosed hypertension are major contributors. The brain doesn’t age—it’s the habits that age it prematurely.”
Understanding that young people can get brain clots is critical for early prevention and treatment.
Symptoms of Brain Clot in Early Stages
Recognizing early brain clot symptoms could mean the difference between full recovery and permanent damage. Here’s how to know if you have a brain clot:
- Sudden and severe headache, unlike anything you’ve felt before
- Numbness or weakness, especially on one side of the body
- Slurred speech or difficulty understanding words
- Blurred or loss of vision in one or both eyes
- Sudden dizziness, loss of balance or coordination
- Difficulty walking or confusion
One of Dr. Vikas’s patients expressed his gratitude, saying:
“Dr. Gupta saved my life when I arrived at his ER with half of my body paralyzed. As his patient, I learned that my addiction to energy drinks and my 14-hour workdays had thickened my blood. After receiving clot-busting drugs and undergoing rehabilitation, he warned me, ‘Your brain is 60, not 28.’ Now, I’m living my life free of any neurological problems and have managed my symptoms through medication and lifestyle changes.”
If any of these signs appear, call emergency services immediately. Time is brain — literally.
Is Blood Clot in Brain Dangerous?
Yes, a blood clot in the brain is dangerous and often life-threatening. The blockage deprives brain cells of oxygen and nutrients, leading to stroke, coma, or permanent neurological damage.
Without fast treatment, brain function can be lost within minutes. Long-term effects may include paralysis, speech difficulties, and memory loss.
How to Remove Blood Clot in Brain Without Surgery
If caught early, a brain clot can often be treated without open surgery. Here’s how:
- Thrombolytics: These are powerful drugs that dissolve clots. They’re most effective within a few hours of symptom onset.
- Anticoagulants: These medications help prevent the clot from getting bigger and reduce the risk of new clots.
- Catheter-directed procedures: In some cases, a small tube is inserted into a blood vessel to reach the clot and either deliver medication directly or extract it.
So, if you’re wondering how to remove blood clot in brain without surgery, the key is early detection and timely medical intervention.
Diagnosis and Recovery
Diagnosing a blood clot in the brain usually involves:
- CT Scan or MRI: To locate and determine the size of the clot.
- Angiography: To see blood flow in the brain.
- Blood Tests: To assess clotting disorders or infections.
Recovery depends on:
- Clot size and location
- How quickly treatment begins
- Age and overall health
Rehabilitation may involve physiotherapy, speech therapy, and cognitive rehabilitation. Many patients recover fully with timely intervention.
Prevention Tips
You can reduce your risk of developing a brain clot with these steps:
- Stay active: Avoid sitting for long hours. Take breaks and stretch every hour.
- Eat healthy: Focus on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and omega-3-rich foods.
- Control chronic conditions: Like diabetes, hypertension, and cholesterol.
- Don’t smoke: And limit alcohol consumption.
Hydrate well, especially during long travel or hot weather.
Final Thoughts
The rise in brain clots is a concerning trend, but with awareness and proactive health management, it can be addressed. Whether you’re young or old, knowing the symptoms of a brain clot in the early stages, acting fast, and adopting preventive habits can make a life-saving difference.
If you suspect a blood clot in the brain, don’t wait. Seek emergency care. With prompt attention, many patients go on to live healthy, fulfilling lives.
FAQs
1: Can young people get brain clots?
Yes, lifestyle habits, hormonal medications, and genetic factors have led to a rise in brain clots among young individuals.
2: How to know if you have a brain clot?
Look for sudden severe headache, slurred speech, confusion, vision loss, or weakness on one side of the body.
3: Can cerebral thrombosis cause stroke?
Yes. Cerebral thrombosis is a type of ischemic stroke caused by a blood clot blocking a brain artery.
4: Can stress cause blood clots in the brain?
You can’t directly get blood clots from stressing, but stress is a contributing risk factor of blood clotting in brain.
5: What are the first signs of a blood clot in the head?
Some of the first signs of blood clot in head are sudden headache, difficulty speaking, numbness or weakness on one side of the body, and vision problems.
Explore more blogs: What are the 5 warning signs of stroke?
